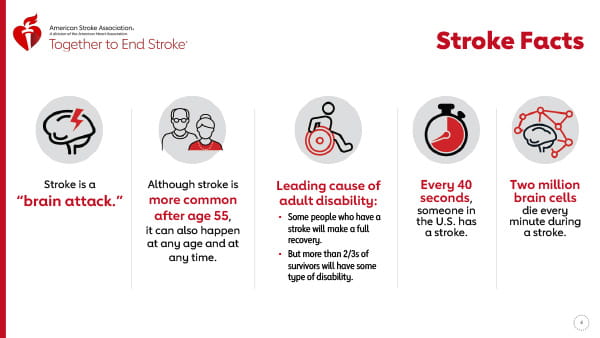
TIA, or transient ischemic attack, is a medical condition that often goes unnoticed or is mistaken for something less serious. However, it is essential to understand that TIA is a warning sign of a potential stroke. During a TIA, blood flow to the brain is temporarily disrupted, causing temporary symptoms that may include weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking. While these symptoms may resolve on their own within a few minutes to hours, it is crucial not to ignore them.
In this article, we will delve into the world of TIA, exploring its causes, symptoms, and potential risk factors. We will also discuss the importance of seeking medical attention promptly and the steps one can take to prevent a full-blown stroke. By understanding TIA and its implications, we can empower ourselves and others to take proactive measures to protect our brain health. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries surrounding TIA.
What is TIA?
TIA, also known as transient ischemic attack, is a medical condition that is often overlooked or mistaken for something less serious. It is crucial to understand that TIA is actually a warning sign of a potential stroke.
TIA occurs when there is a temporary disruption in blood flow to the brain, usually caused by a blood clot or a narrowing of the blood vessels.
These disruptions are brief, lasting for only a few minutes, but the effects can be alarming and may mimic those of a stroke.
During a TIA,
symptoms such as sudden weakness, numbness, or paralysis on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, and loss of vision in one or both eyes may occur. However, unlike a stroke, these symptoms typically resolve within 24 hours.
Seeking immediate medical attention is essential when experiencing symptoms of a TIA. Even though the effects may be temporary, it is crucial to receive prompt medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and prevent the occurrence of a full-blown stroke.
TIA can be a warning sign of blood vessel damage or other underlying health issues.
Risk factors for TIA include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, and a family history of stroke. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps towards preventing strokes and maintaining optimal brain health.
Types of TIA
There are no specific types or classifications of TIA. However, it is important to note that TIA is a warning sign of a potential stroke, which can be categorized into two main types: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
- Ischemic Stroke: This type of stroke occurs when a blood clot or plaque buildup blocks a blood vessel in the brain, cutting off the blood supply and oxygen to the affected area.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: This type of stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding and damage to the surrounding brain tissue.
While the symptoms and treatment may vary, both types of stroke require immediate medical attention.
Practical Applications and Future Developments
The practical application of understanding TIA lies in its potential to serve as a warning sign for stroke. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical evaluation promptly, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent a full-blown stroke and protect their brain health.
Causes of TIA
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is typically caused by a temporary disruption in blood flow to the brain. The most common cause is a blood clot that forms in an artery leading to the brain or within the brain itself. Other possible causes of TIA include:
- Atherosclerosis: the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries that restrict blood flow.
- Irregular heart rhythm: such as atrial fibrillation, which increases the risk of blood clots.
- High blood pressure: which can damage blood vessels and lead to clot formation.
- Smoking: which damages blood vessels and increases the risk of clot formation.
It’s important to note that TIA is a warning sign of a potential stroke. Understanding the causes can help individuals take preventive measures and seek appropriate medical care.
Symptoms of TIA
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), often referred to as a mini-stroke, shares similar symptoms to a full-blown stroke. These symptoms occur suddenly and last for a short duration, typically less than an hour. It’s crucial to recognize these warning signs as they could signify an increased risk of a stroke in the future. The common symptoms of TIA include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, including the face, arm, or leg.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Trouble with vision in one or both eyes.
- Loss of balance, dizziness, or difficulty walking.
- Severe headache, often described as the worst headache of a person’s life.
If anyone experiences these symptoms, it’s vital to seek medical attention immediately. Prompt evaluation and diagnosis can help determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment to prevent a future stroke.
Symptoms of TIA are often the body’s way of providing a warning sign. Identifying and addressing the causes of TIA can greatly reduce the risk of a full stroke, allowing individuals to take preventive measures for a healthier future.
Risk Factors for TIA
TIA (
Transient Ischemic Attack), also known as a mini-stroke, can occur due to various risk factors. Understanding these factors is crucial in assessing an individual’s susceptibility to a TIA.
Here are
some key risk factors associated with TIA:
- High blood pressure: Hypertension significantly increases the risk of TIA.
- Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels, making them more prone to blockages.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels contribute to the development of TIA.
- High cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to plaque buildup, causing TIA.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of TIA.
- Atrial fibrillation: This heart condition can cause blood clots that may lead to TIA.
- Age: The likelihood of TIA increases with age, especially after 55 for men and 60 for women.
- Family history: Having a family history of stroke or TIA elevates the risk.
It is important to note that addressing these risk factors can greatly reduce the chances of experiencing a full-blown stroke in the future. Taking preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes and medication, can significantly mitigate the risk associated with TIA.
Importance of Seeking Medical Attention
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Seeking professional help is crucial as it can help determine the underlying cause and prevent a major stroke. Without
proper medical evaluation, individuals are at a higher risk of experiencing a
full-blown stroke in the future.
Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce the chances of further complications or disabilities.
Common reasons to seek medical attention:
- Symptoms of TIA: Recognizing the signs of TIA, such as sudden weakness, numbness, or slurred speech, should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
- Underlying risk factors: Understanding and addressing the risk factors associated with TIA, including high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes, is crucial for comprehensive medical care.
- Prevention of future health issues: Seeking medical attention enables individuals to address their overall health and make necessary lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of future strokes.
Remember,
time is of the essence when it comes to TIA. Delaying medical attention may increase the likelihood of a major stroke. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of TIA, don’t hesitate to contact a healthcare professional immediately.
- American Stroke Association
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Stroke
Preventing a Stroke
To prevent a stroke, it’s essential to take proactive measures. Here are some key steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Managing high blood pressure: Elevated blood pressure is a significant risk factor for stroke. Regular monitoring, and appropriate lifestyle changes can help keep blood pressure under control.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of stroke. By quitting smoking, individuals can lower their chances of experiencing a stroke.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity and excess weight can contribute to various health issues, including stroke. A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial for maintaining a healthy weight.
- Seeking treatment for heart conditions: Conditions like atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat) can raise the risk of stroke. Timely treatment, including medication or surgical intervention, can mitigate this risk.
- Controlling diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and increase the likelihood of stroke. Regular monitoring, medication adherence, and a healthy lifestyle can help control diabetes effectively.
It’s important to note that these steps not only reduce the risk of stroke but also promote overall health and well-being. By incorporating these strategies into their lifestyles, individuals can empower themselves to lead healthier lives.
For additional information and resources about stroke prevention, individuals are encouraged to consult their healthcare provider or visit reputable medical websites such as the American Heart Association or the National Stroke Association.
Conclusion
Seeking immediate medical attention for a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is crucial in order to identify the root cause and prevent a major stroke. This article has highlighted the significance of taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of stroke, including managing high blood pressure, quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, seeking treatment for heart conditions, and controlling diabetes. These measures not only decrease the likelihood of a stroke but also promote overall well-being.
To further explore stroke prevention, individuals are encouraged to consult their healthcare provider or reputable medical websites. By staying informed and implementing these preventive measures, individuals can significantly lower their risk of experiencing a TIA or stroke. Remember, taking care of one’s health is a lifelong commitment that leads to a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the importance of seeking immediate medical attention for Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)?
A: Seeking immediate medical attention for TIA is important because it helps determine the underlying cause and prevents a major stroke.
Q: How can individuals reduce their risk of stroke?
A: Individuals can reduce their risk of stroke by managing high blood pressure, quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, seeking treatment for heart conditions, and controlling diabetes.
Q: Do these steps only reduce the risk of stroke?
A: Yes, these steps not only reduce the risk of stroke but also promote overall health and well-being.
Q: Where can individuals find additional information and resources on stroke prevention?
A: Individuals are encouraged to consult their healthcare provider or visit reputable medical websites for additional information and resources on stroke prevention.